PCB relay, or printed circuit board relay, refers to a device that is mounted on a PCB. It is an electrically operated switch used to control a high-power circuit with the aid of a low-power signal. PCB relays are used in numerous electronic systems and devices based on their minimal size, reliability, and ease of use.
The primary components of a PCB relay include:
Coil: The coil generates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it.
Armature: Armature: It is a moving component which is attracted to the magnetic field that is created by the coil.
Contacts: The contacts are the points where the electrical connection is made or broken.
Spring: The spring returns the armature to its original position upon the coil being de-energized.
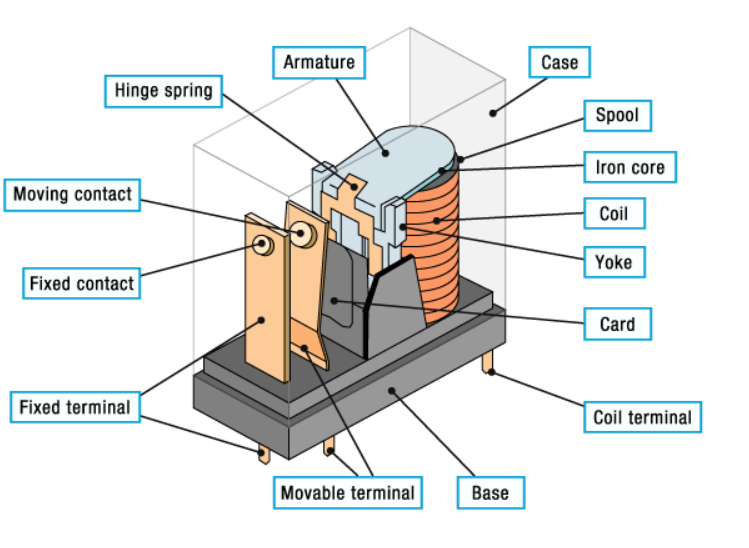
PCB relays function on the principles of electromagnetism. The phenomenon of a magnetic field being generated when current passes through a coil is well documented. This action attracts the armature, which in turn moves to connect or disconnect the circuit at the contacts.
A magnetic force from the coil pulls the armature downwards as the relay is powered, closing the contacts and allowing current to flow in the associated circuit. The spring opens the contacts and breaks the current flow as the coil is de-powered by returning the armature to the original position.
PCB relays can also be constructed to have varying switching configurations, including normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC). In the case of a normally open configuration, the contacts remain open upon de-energizing and close upon being energized. In a normally closed configuration, the contacts are closed in the event of de-energizing and open in the event of energizing.
Electromechanical Relays
Electromechanical relays are the most common type of PCB relays.They are made up of contacts, armature, and coil. Relays of this type are renowned for their dependability and capacity to manage high voltages and currents.
Solid-State Relays
Solid-state relays (SSRs) do not have any moving parts and rely on semiconductors to control the flow of current. They offer faster switching speeds, longer lifespan, and higher reliability compared to electromechanical relays.
Reed Relays
Reed relays comprise a pair of ferromagnetic contacts (reed switches) encased within a glass tube. They are driven by an external magnetic field and are recognized for their rapid switching rates and enhanced insulation resistance.
Hybrid Relays
Hybrid relays combine the features of both electromechanical and solid-state relays. They have the advantages of high current handling capacity and quick switching speeds.
SPDT
The SPDT relay features a single pole with two throw positions. It can connect one terminal to either of two conducting positions. One set of contacts stays closed while the other stays open in SPDT relays' two states, and vice versa. SPDT relays are ideal for situations where you need to be able to switch between two different circuits.
SPST
The SPST relay is a single pole, single throw relay. The pole has one throw position and can only regulate one circuit. Relays of this kind are often used to turn lights and gadgets on and off.
DPST
The DPST relay is a double pole, single throw relay.It is composed of two independent single-throw circuits, each of which has a fixed contact and a movable contact. This makes the relay helpful for applications that need synchronized control of multiple circuits since it enables it to control two independent circuits at once.
DPDT
The DPDT relay is a double pole, double throw relay.It has two throws and two poles, so each pole can link to two different throws. This lets the relay manage more than one circuit and do more complicated switching tasks, like switching between different circuit layouts. DPDT relays are used in a lot of different electrical systems, especially when two circuits need to be switched at the same time.
High reliability
PCB relays are intended to offer stable operation for a significant period of time. They are constructed to function under different environmental conditions and are used in important applications where reliability is the key consideration.
Compact Size
PCB relays also come in reduced-size versions, which make them well suited for applications in space-limited electronic systems. They can save board space due to their minimal footprint.
Accurate Control
PCB relays can control the electrical circuits with accuracy. They can be actuated using low control signals and switch the high-power loads with accuracy.
Long Lifespan
Well-designed and used PCB relays can enjoy a long service life. They can sustain many switching cycles with minimal loss of operational efficiency.
Automotive Electronics
PCB relays are used in a wide range of applications in the automotive industry to control different systems such as headlights, windshield wipers, and fuel pumps. They offer secure switching and protection to these key components.
Industrial Automation
PCB relays are utilized in industrial applications to operate motors, solenoids, and various actuators. They are crucial to the automation system since they provide precise control and synchronization of processes.
PCB relays are utilized in several consumer electronic devices, including air conditioners, washing machines, and refrigerators. They act to regulate and allocate power to diverse operations within these devices.
Telecommunications
In the telecommunication industry, PCB relays are used to switch and route signals in the equipment of a network. They provide secure connections as well as effective signal delivery.
Home Appliances
PCB relays are used in most household appliances like microwaves, ovens, and coffee makers. They enable the control of functional components, such as the heat elements and the timers.
Electrical Specifications
In choosing a PCB relay, the electrical specifications like operating voltage, current rating, and power capacity would need to be considered. These need to match the requirements of the application to enable optimal operating conditions.
Mechanical Specifications
The mechanical parameters including the contact resistance, the insulation resistance, and the switching speed have to be evaluated in relation to the specific requirements of the application.
Environmental Concerns
The conditions of operation have to be taken into account. The temperature, humidity, and vibration level can affect the reliability and the life of the relay. It is critical to use the proper relay for the operating conditions of the surrounding environment.
Application Requirements
The application's specific requirements, including the nature of the load being controlled and the frequency of switching, will dictate the selection process. Various types of relays might be better suited for specific applications.
Cost and Reliability
It is essential to balance cost versus reliability. Although high-reliability relays will cost more, they can save money in the long term by lowering maintenance and replacement costs.
In conclusion, PCB relays are essential for the control of power circuits using low-power signals. They have different types and provide benefits such as reliability and minimal size, thus being utilized in the automotive, industrial, consumer electronic, and telecommunication applications. The knowledge of their principles and types assists in the selection of the correct relay for particular applications.